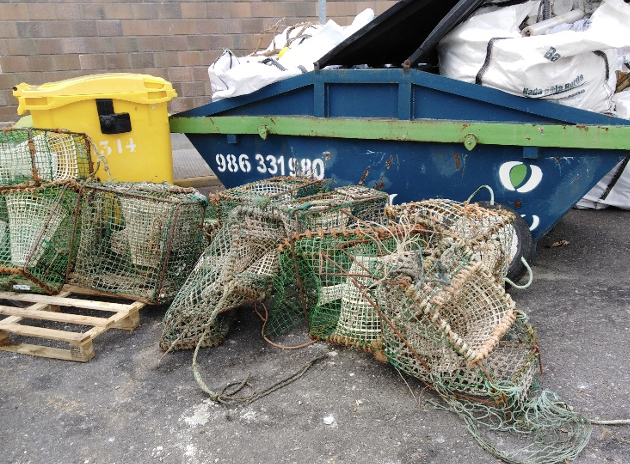
Fishing port of Dunmore East
A busy fishing harbour, home to a sailing club food shop/ smoke house, seafood shop, adventure facility, sailing club, coast guard, tour operators, boat yard, RNLI Lifeboat, net mending facility and a BIM ice plant.
Fishing practice: 12 regular boats under 24m,
Mostly bottom trawls, 1 x beamer trawl, 2 x pure seines Landings: White fish – Hake, Haddock, Whiting